Thursday, April 28, 2011
Introduction to WAN protocols
Do you like this story?
Wide Area Networks (WANs) operate over serial links. A serial link is one that transmits and receives digitized signal one bit at a time. Serial links using modems typically offer 56Kbps. Compare a serial link with that of a parallel link. An example of parallel link is printer connection over parallel cable. A printer receives several bits at a time and processes them all. A parallel line is typically used for connecting your monitor, printer, and CDROM drive. Parallel links run over over a very short distances. Within serial links, there are two types:
|
Asynchronous serial links: These are widely used for connecting to Internet using your dial-up modem. Asynchronous link is normally used for low speed communications.
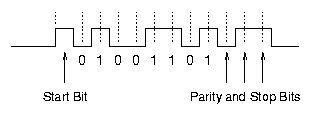
Async (short for Asynchronous) links require start and stop bits for effective communication. It can also have parity bits for error checking. When using Async communication link, both sender and receiver need to agree on fixed line speed (expressed in terms of bits per second), otherwise, the receiver may not be able to receive any data at all.
2. Synchronous serial links: Synchronous links, as the name suggests use clocking to transmit or receive data. A clock signal is required for transmitting or receiving synchronous data.
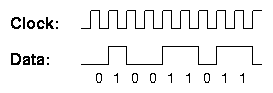
The clock signal may be transmitted separately, or could be derived from the received signal. In either case, the clock signals are used for receiving the data.
Synchronous links can operate at very high speeds. SDLC, and HDLC are examples of synchronous link protocols.

This post was written by: Techie Blogger
Techie Blogger is a IT Trainer, Pro Blogger and front end web developer. Follow him on Twitter






0 Responses to “Introduction to WAN protocols”
Post a Comment